Introduction
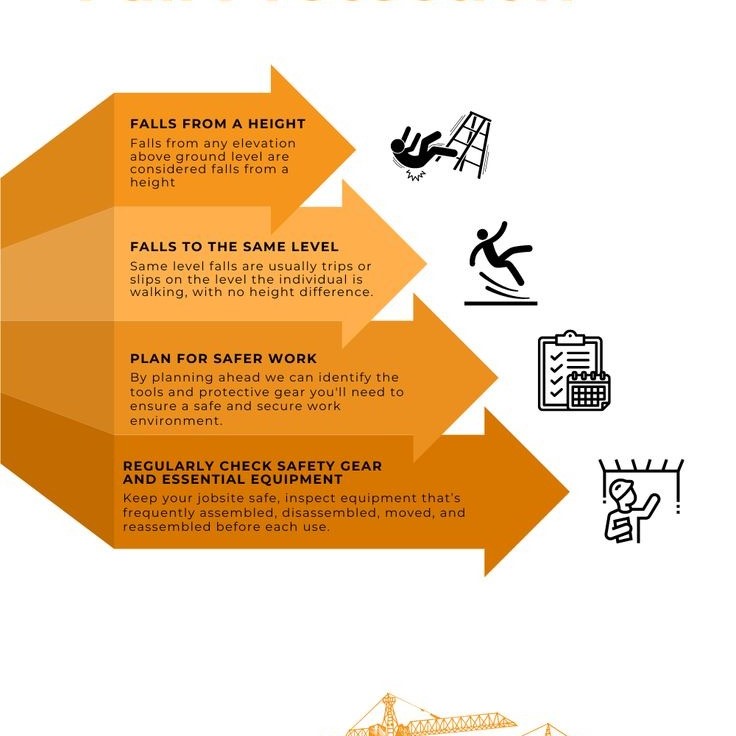
Fall protection plan is essential for workplace safety. They prevent injuries and ensure employees work securely at heights. A well-designed plan protects both workers and employers from accidents.
Importance of Fall Protection in the Workplace
Fall protection is vital across industries. Falls are among the leading causes of workplace injuries. In construction, industrial roles, and maintenance work, workers frequently face height-related risks. Implementing a fall protection plan minimizes these risks effectively.

Employers must prioritize a safety-first culture. Adequate fall protection reduces injury rates and boosts employee morale. This approach helps meet legal requirements, avoiding non-compliance penalties.
Key Objectives of a Fall Protection Plan
A fall protection plan serves several primary goals:
- Identify Hazards: Assess and address potential fall hazards systematically.
- Protect Employees: Implement methods to safeguard workers against falls.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure adherence to OSHA standards and other relevant guidelines.
- Emergency Preparedness: Establish procedures for immediate response in case of accidents.
By focusing on these objectives, employers can create safer environments. Proper planning reduces workplace disruptions and enhances operational reliability.
OSHA Standards for Fall Protection
Fall protection plans must comply with specific OSHA standards. OSHA ensures workplace rights and safety. Compliance protects employees and helps employers avoid legal issues.
Overview of OSHA Requirements
OSHA sets stringent guidelines for fall safety. Employers must ensure workers have secure environments at heights. Key points include:
- Height-Based Requirements: Fall safeguards must be in place for heights above 6 feet in construction or 4 feet in general industry.
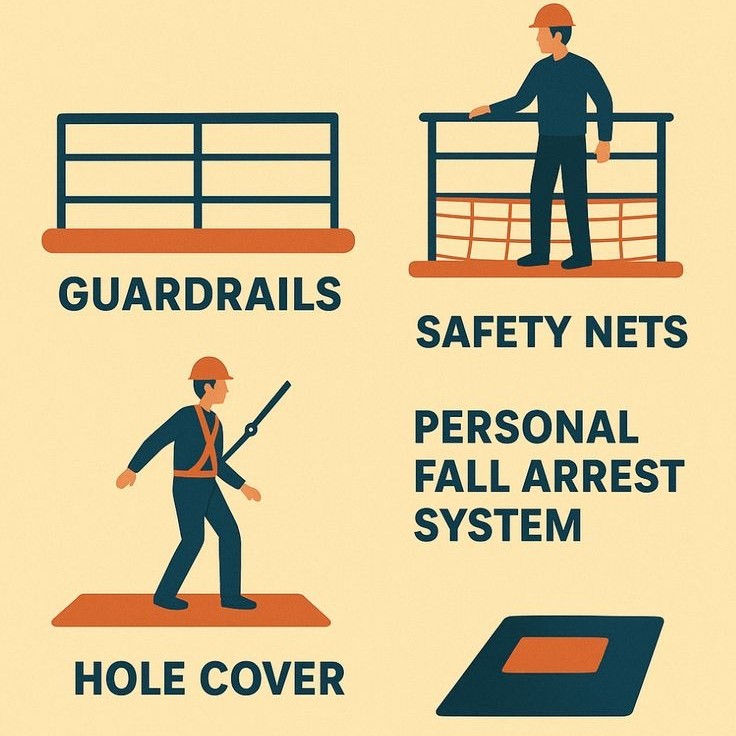
- Equipment Standards: OSHA mandates the proper use of fall protection systems like guardrails, safety nets, and personal safety gear.
- Training: Employers must train workers on hazard recognition and equipment use.
- Inspection: Regular inspection and maintenance of fall prevention systems are required.
- Emergency Protocols: Employers need ready procedures for fall-related emergencies.
Compliance ensures safer workplaces and avoids penalties. Employers should stay updated on OSHA revisions and industry-specific rules.
When Employers Must Implement a Fall Protection Plan
A fall protection plan is mandatory under certain conditions, including:
- Construction Activities: OSHA requires fall protection when workers operate at heights above 6 feet.
- Industrial Sites: General industry jobs with risks above 4 feet must follow fall protection measures.
- Hazardous Environments: Employers must address fall risks in unique settings, like scaffolds or confined spaces.
- Risk Assessments: Employers should evaluate conditions and implement plans where fall risks are significant.
Proper planning not only meets regulations but also saves lives. Employers benefit from smoother operations and reduced liabilities by adhering to these standards.
Essential Components of a Fall Protection Plan
Creating a comprehensive fall protection plan involves key components designed to ensure safety. Effective planning minimizes fall risks and prepares workplaces for potential emergencies.
Hazard Assessment and Site Evaluation
Hazard assessment is the first step in fall protection planning. Employers must evaluate workplaces for fall risks. Identifying hazards, such as unguarded edges or weak surfaces, is crucial. Site evaluations should be performed regularly to account for changes in the work environment.
Selection and Use of Fall Protection Systems
Choosing the right fall protection system is essential. Employers should match systems to specific workplace risks. Common solutions include guardrails, safety nets, and harnesses. These tools must meet OSHA standards and be used as recommended. Proper use ensures maximum protection for workers.
Training Requirements for Workers
Training helps workers understand safety practices and equipment use. Employers must ensure all workers are trained before working at heights. Sessions should cover hazard recognition, fall prevention systems, and emergency protocols. Updated training keeps workers informed of new regulations.
Emergency and Rescue Procedures
Emergency procedures must be part of every fall protection plan. Employers should develop clear rescue strategies for fall incidents. Quick response plans can save lives and reduce injury severity. Workers must receive training on responding to fall-related emergencies effectively.
Employers who incorporate these components create safer work environments. Comprehensive plans save lives, enhance productivity, and ensure OSHA compliance.
Common Fall Hazards in the Workplace
Fall hazards are prevalent in many workplaces. They vary across industries and job types. Identifying and understanding these hazards is critical for effective fall protection plans. Employers must evaluate site-specific risks to address fall dangers effectively.
Construction Industry Fall Risks
Falls are a leading hazard in construction. Workers often face risks from heights. Common dangers include:
Unguarded Edges
- Definition of Unguarded Edges: Open-sided floors refer to areas within a construction site that lack barriers or protective railings. These locations can lead directly to significant falls if proper precautions are not taken.
- Fall Risks: The absence of guardrails or other protective measures dramatically increases the likelihood of accidental slips and falls. Workers can easily lose their balance or miscalculate their movements when near unprotected edges.
- Statistics: Falls from unguarded edges are among the leading causes of serious injuries in construction. Research shows that many incidents arise from workers unintentionally stepping off open sides without protection.
- Prevention Measures: To mitigate the risks associated with unguarded edges, construction sites should implement stringent safety protocols. This can include the installation of guardrails, warning signs, and designated safe zones for workers moving near edges.
Scaffolding Hazards
- Importance of Proper Setup: Scaffolding systems are essential for providing temporary access and support during construction. However, if they are not set up correctly, they can pose significant dangers to workers.
- Examples of Hazards: Common hazards include weak scaffolding materials, insufficient bracing, and failure to follow manufacturer guidelines during assembly. Such faults can compromise the entire structure, leading to collapses or instability.
- Consequences of Malfunction: Workers on improperly erected scaffolds may experience sudden falls, resulting in serious injuries or fatalities. Scaffolding accidents can disrupt work projects and lead to costly legal issues for employers.
- Best Practices: Regular inspections, following safety regulations, and providing training on proper scaffold assembly and use are vital for preventing scaffolding-related accidents on construction sites.
Ladders
- Types of Ladder Hazards: Issues such as slippery surfaces, damaged rungs, and improper ladder placement can significantly increase the chances of a fall while using ladders on job sites.
- Consequences of Ladder Falls: Falls from ladders can lead to severe injuries, including fractures, sprains, and head trauma. Many workers may underestimate the risks associated with ladder use, thinking they can manage without proper safety measures.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular inspections are necessary to identify and repair any deterioration on ladders, such as cracks, loose rungs, or worn-out feet. Ensuring that ladders are in good condition helps mitigate hazards.
- Safe Usage Practices: Workers should receive training on proper ladder techniques, including setting up ladders on stable ground, maintaining three points of contact, and selecting the right ladder height for the job.
Roof Work
- Inherent Risks of Roof Work: Working on roofs without adequate protection can expose workers to significant falls. Many roofing tasks require individuals to navigate steep slopes or unguarded edges, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Weather Influences: Slippery surfaces due to rain, snow, or ice further complicate roof work, affecting traction and balance. Weather conditions can quickly change, creating unforeseen hazards.
- Lack of Safety Measures: Some workers may neglect to use safety harnesses or fail to implement proper tie-off points, which can lead to severe consequences if a fall occurs.
- Preventive Strategies: To reduce risks while working on roofs, projects must include comprehensive safety plans. This involves using safety guardrails, providing harnesses, and ensuring workers receive thorough training on fall protection measures specific to roofing tasks.
Employers should utilize fall protection systems like guardrails and safety harnesses. Regular training for workers is vital to mitigate these risks effectively.
Industrial and Maintenance Work Hazards
Industrial and maintenance workplaces also present fall risks. Common hazards here include:
- Slippery Floors: Spilled liquids or polished surfaces increase the chance of slips and falls.
- Uneven Spaces: Damaged floors or areas with unexpected gaps create fall hazards.
- Confined Spaces: Limited movement areas, such as tanks, pose unique dangers.
- Machinery Access: Maintaining machines at height can be hazardous without proper safeguards.
Employers should ensure all floors are regularly inspected for risks. Non-slip surfaces and proper signage enhance workplace safety. Additionally, workers must be briefed on site-specific hazards and trained to use fall protection devices.
Identifying and addressing these fall hazards is the foundation for reducing injuries. Comprehensive planning keeps workers safe and operations efficient.
How to Create an Effective Fall Protection Plan
Creating an effective fall protection plan is vital for workplace safety. A proper plan prevents injuries, ensures compliance, and fosters a secure working environment.
Steps to Develop a Comprehensive Plan
- Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment: Identify all potential fall hazards at the worksite. Evaluate areas such as elevated surfaces, scaffolds, and confined spaces.
- Define Safety Objectives: Clearly outline the goals of your fall protection plan. Focus on reducing hazards, meeting OSHA standards, and preparing for emergencies.
- Choose Appropriate Protection Systems: Select gear and equipment that matches identified risks. Use OSHA-approved guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems.
- Develop Emergency Procedures: Create detailed rescue plans for fall-related incidents. Ensure protocols are practical and easy to follow during emergencies.
- Formulate a Training Program: Train all employees on hazard recognition, equipment use, and emergency protocols. Update training sessions as workplace conditions or OSHA rules change.
- Document the Plan: Write down every aspect of the plan. Include risk assessments, system details, emergency actions, and compliance steps.
- Test and Review: Conduct regular inspections to ensure the plan works effectively. Adjust as needed to maintain safety standards.
Best Practices for Implementation and Maintenance
- Involve Workers in Planning: Engage employees to gather insights about job-specific risks. Worker input can make plans more practical and effective.
- Prioritize Regular Inspections: Continuously inspect fall protection systems and equipment. Replace worn-out gear immediately to avoid accidents.
- Use Clear Signage: Install signs warning about potential fall hazards. Labels and instructions boost awareness and safety.
- Maintain Open Communication: Encourage workers to report hazards or issues. A culture of open dialogue fosters vigilance.
- Update Plans Frequently: Revise the plan when new regulations or workplace changes arise. A dynamic approach reduces risks.
By following these steps and best practices, employers can create comprehensive fall protection plans. Such plans enhance safety and ensure legal compliance.
Legal and Financial Implications of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with OSHA standards can lead to severe consequences. Employers face legal, financial, and operational risks. Understanding these implications ensures businesses prioritize workplace safety and avoid penalties.
Penalties for Failing to Meet OSHA Standards
Failing to meet OSHA’s fall protection requirements can result in substantial penalties. Key penalties include:
- Fines: OSHA imposes significant fines for non-compliance. These fines vary based on the severity of the violation. For repeated or willful violations, penalties are higher.
- Legal Actions: Non-compliance may lead to lawsuits from injured employees or their families. These legal battles can damage a company’s reputation and finances.
- Work Stoppages: OSHA violations may force temporary closures to address safety deficiencies. This disrupts operations and causes revenue losses.
- Criminal Charges: Severe negligence or willful disregard for safety can result in criminal investigations. Employers and managers may face personal liabilities.
Adhering to OSHA standards prevents these penalties. It also protects employees and promotes a safer workplace.
Cost Benefits of Proper Fall Protection Planning
Investing in a solid fall protection plan delivers significant cost-saving benefits. Key advantages include:
- Reduced Accidents: A well-implemented plan minimizes workplace injuries. Fewer injuries lower compensation claims and medical costs.
- Compliance Savings: Companies that meet OSHA standards avoid hefty fines and legal fees.
- Insurance Premium Reduction: With fewer accidents, businesses can negotiate lower insurance premiums over time.
- Improved Productivity: Safe workplaces boost employee morale and efficiency, reducing absenteeism and enhancing output.
- Reputation Enhancement: Complying with safety laws builds trust with employees, clients, and industry stakeholders.
Prioritizing fall protection measures protects lives and secures financial stability for businesses. Proactive safety measures ensure compliance and long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fall Protection Plans
Typical Misunderstandings and How to Avoid Them
Fall protection plans are essential but often misunderstood. Addressing common misconceptions ensures better compliance and safety. Below are some typical misunderstandings and ways to avoid them:
- “Fall protection is only needed for construction work.”
- Fact: OSHA requires fall protection for many industries, including maintenance and general industry.
- Solution: Review OSHA’s guidelines for your specific industry to ensure compliance.
- “Personal protective equipment (PPE) is enough.”
- Fact: PPE is only one part of a comprehensive fall protection plan.
- Solution: Combine PPE with training, hazard assessment, and emergency procedures.
- “All training sessions are the same.”
- Fact: Training must address site-specific risks and current OSHA rules.
- Solution: Tailor training to your unique work environment and update it regularly.
- “Only high-risk jobs require fall protection plans.”
- Fact: Even small fall risks can cause injuries.
- Solution: Evaluate fall risks for every worksite, no matter the perceived risk level.
Avoiding these misunderstandings improves workplace safety and ensures your fall protection plan is effective.
Clarifications on Compliance Challenges
Meeting fall protection standards can be challenging for employers, especially with changing regulations. Here are some common compliance challenges and ways to address them:
- Staying Updated on OSHA Rules:
- Challenge: OSHA standards evolve, making it hard to stay compliant.
- Solution: Regularly check OSHA updates and industry-specific safety requirements.
- Implementing Consistent Training:
- Challenge: Employees may skip or forget safety protocols over time.
- Solution: Schedule regular refresher training sessions addressing fall prevention and protection systems.
- High Costs of Safety Equipment:
- Challenge: Quality fall protection systems can be expensive.
- Solution: Invest in durable, OSHA-approved equipment that provides long-term safety benefits.
- Emergency Response Readiness:
- Challenge: Companies may lack actionable rescue plans for fall incidents.
- Solution: Develop and rehearse emergency procedures so all workers understand their roles.
- Limited Workplace Awareness:
- Challenge: Workers might not recognize hazards or understand proper equipment usage.
- Solution: Conduct frequent hazard assessments and encourage employees to report risks.
Clarifying and addressing these challenges ensures smoother compliance with fall protection standards. Employers who remain proactive can protect their workers and avoid penalties.
Conclusion
Summary of What Employers Need to Know
Employers must prioritize fall protection to ensure workplace safety and legal compliance. A comprehensive fall protection plan saves lives and reduces liabilities. It includes risk assessments, suitable equipment, training, and emergency procedures. OSHA requires strict adherence to its standards to prevent injuries and penalties. Employers should stay updated on regulations and industry best practices to maintain compliance.
Final Tips for Ensuring Workplace Safety
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Frequently evaluate the workplace for potential fall hazards.
- Update Training Programs: Regularly educate employees on new regulations and safety procedures.
- Invest in Quality Equipment: Ensure all fall protection systems meet OSHA standards.
- Encourage Reporting Hazards: Create an environment where workers feel safe to report risks.
- Review Plans Often: Revise fall protection plans as workplace conditions or safety rules change.
Commitment to safety fosters a productive and compliant workplace. Employers who prioritize fall protection build trust and prevent accidents.