Introduction to Fall Protection
The hierarchy of fall protection is a crucial framework designed to ensure safety in various workplaces. As more industries recognize the risks associated with falls, having a comprehensive understanding of fall protection systems becomes essential. This guide aims to delve into the hierarchy of fall protection, providing detailed insights for 2025 workers. By understanding how to protect themselves and their colleagues effectively, employees can minimize risks and prevent accidents in the workplace.
What is Fall Protection?
Fall protection refers to safety measures aimed at preventing accidental falls in workplaces. It includes equipment, processes, and policies that reduce fall risks. Employees facing height-related hazards must use fall protection systems like guardrails, safety nets, and harnesses. Its purpose is to safeguard lives and maintain productivity.
Fall protection also encompasses proper training to ensure workers use equipment correctly. Employers are responsible for assessing risks and implementing fall prevention strategies. By understanding needs and hazards, proper systems can be chosen effectively.
Importance of Preventing Workplace Falls
Preventing workplace falls is vital for ensuring employee safety and avoiding injuries. Falls are among the leading causes of workplace accidents globally. Injuries from falls impact productivity and morale and may lead to costly compensation claims.
Implementing fall protection strategies helps avoid downtime and keeps processes on track. Being proactive not only saves lives but also maintains the company’s reputation. Employers should identify risks, train workers, and adhere to safety regulations.
A safe workplace enhances trust and boosts engagement, emphasizing the importance of fall prevention for overall well-being.
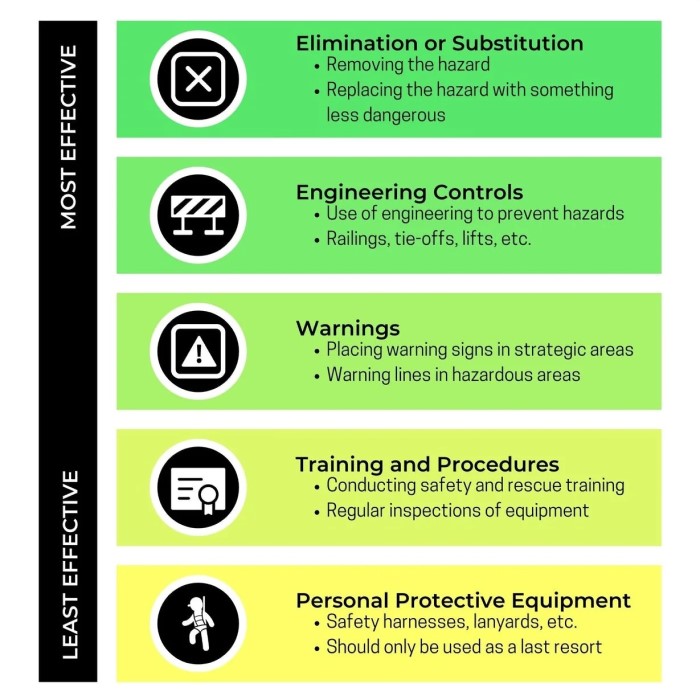
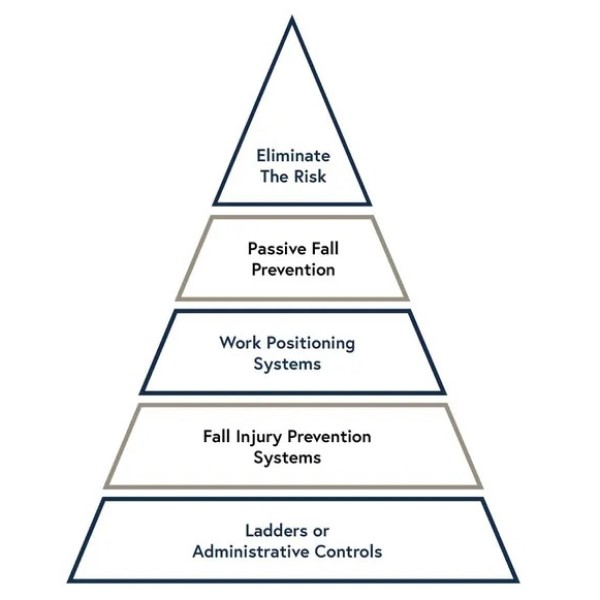
The Hierarchy of Fall Protection Explained
The hierarchy of fall protection is a structured approach to reduce workplace falls effectively. It provides a clear sequence of measures to address fall hazards systematically. This strategic model helps employers create safer environments, safeguard employees, and meet legal requirements. Understanding the hierarchy enables organizations to prioritize safety and manage risks efficiently.
Overview of the Hierarchy Levels
The hierarchy of fall protection consists of several levels to manage fall hazards:
- Elimination: The best method to prevent falls is to remove hazards. Eliminating the source of risks ensures workers‘ safety without requiring additional equipment.
- Passive Fall Protection Systems: If elimination is not feasible, passive systems come next. These include guardrails, safety nets, and barriers that physically block falls without requiring active participation.
- Fall Restraint Systems: These systems ensure workers stay within a safe area by restricting their movement at heights.
- Fall Arrest Systems: Fall arrest systems prevent injury if a fall occurs. Components like harnesses and lanyards are used to stop falls safely.
- Administrative Controls and Training: Proper oversight and training ensure workers follow protocols and are aware of risks.

This hierarchy encourages prioritizing prevention over reaction, ensuring effective safety strategies.
Why a Hierarchical Approach is Essential
A hierarchical approach is vital for managing fall hazards systematically and effectively. It prioritizes prevention, starting with eliminating risks, followed by passive and active solutions. This sequence ensures the highest possible level of safety for workers.
By using a hierarchy, employers can identify and apply the most effective measures first. Eliminating hazards is the most reliable form of protection, as it removes risks completely. Passive systems then address risks without worker involvement, making them safer and easier to manage.
Active systems such as fall restraint and arrest devices require worker participation but are necessary when other methods are not possible. Finally, training and administrative controls improve workers’ awareness and adherence to safety rules, completing the safety strategy.
This approach reduces injuries, improves morale, and aligns businesses with legal standards like OSHA and ANSI regulations. Implementing the hierarchy shows dedication to worker safety and workplace excellence.
Elimination: The First Line of Defense
Elimination is the most effective step in the hierarchy of fall protection. It involves proactively identifying and addressing hazards before they pose a threat to workers. By removing or avoiding potential fall risks altogether, organizations can achieve the highest level of safety.
Employers must evaluate the workplace meticulously, looking for conditions that could lead to falls. This includes analyzing work processes, physical structures, and tasks carried out at heights. Once hazards are identified, immediate action should follow to eliminate them completely.
Identifying and Removing Fall Hazards
The first step in elimination is recognizing potential fall hazards. Common hazards include uneven floors, unprotected edges, open holes, slippery surfaces, and unstable walking platforms. Conducting regular inspections and risk assessments helps catch hazards early.
Once identified, employers need to resolve these issues by making adjustments or changes. For instance:
- Structural Modifications: Modify the layout of workspaces by removing dangerous edges or unstable platforms.
- Workflow Changes: Adjust how tasks are performed to avoid unnecessary exposure to heights.
- Design Solutions: Create workspaces designed to minimize fall risks, using safer equipment or building features.
Employers should involve workers in identifying hazards as they are more familiar with their work environments. Additionally, proper documentation of identified hazards ensures systematic elimination.
Practical Examples of Fall Hazard Elimination
Several strategies exist to eliminate fall hazards:
- Relocation of Tasks: Move tasks from heights to ground level to avoid the need for climbing.
- Installation of Equipment: Use tools or machinery to complete high-risk jobs from a safer location.
- Redesign Workspaces: Modify workplace design to eliminate the need for working at elevated levels.
- Use of Technology: Implement automation or robotic systems to handle tasks that pose fall risks.
In construction, eliminating fall hazards might involve redesigning roofs so workers don’t need to step near edges. In manufacturing, installing permanent guardrails at elevated areas may remove potential hazards entirely.
Elimination is vital because it reduces the reliance on protective equipment that can fail or require monitoring. By removing hazards at the source, workers can operate in safer environments without additional preventive measures. This step underscores the importance of creating a workplace culture focused on safety first.
Passive Fall Protection Systems
Passive fall protection systems form a critical layer within the hierarchy of fall protection. These systems are designed to work automatically, without requiring worker intervention. Their primary role is to create physical barriers that prevent falls at workplaces.
Passive systems are prevalent because they reduce human errors and enhance safety. They are stationary, reliable, and require minimal ongoing involvement. By incorporating well-designed passive systems, workplaces can significantly lower fall-related risks and injuries.
Role of Passive Systems in the Hierarchy
Passive systems serve as the second level in the hierarchy of fall protection. They are implemented when eliminating hazards is not possible. These systems ensure safety with minimal dependence on workers’ actions, providing a proactive solution to prevent accidents.
Passive systems are favored in situations where high-risk environments make worker mistakes more likely. They act as the foundation of safety measures, complementing other strategies like fall restraint and arrest systems.

The use of passive systems simplifies safety protocols and fosters confidence among employees. By blocking hazards physically, they reduce the likelihood of incidents and help maintain smooth operations. Employers using passive systems demonstrate their commitment to safety and regulatory compliance.
Examples: Guardrails, Safety Nets, and Barriers
Passive fall protection systems typically include:
- Guardrails: Guardrails are rigid barriers installed at edges or elevated surfaces. They prevent workers from stepping off edges, ensuring optimal safety. Commonly used in rooftops and construction sites, guardrails are highly effective and simple to maintain.
- Safety Nets: Safety nets catch workers who slip or fall, minimizing injury impact. They are often installed beneath work areas, such as under scaffolds or bridges. Safety nets provide protection against injury while allowing freedom of movement during work.
- Barriers: Temporary or permanent barriers block access to hazardous areas. Examples include fencing around dangerous zones or gates at elevated tasks. Barriers ensure workers avoid risky areas altogether, which significantly reduces fall potential.
Employers should ensure these systems meet industry standards, follow proper installation procedures, and conduct routine inspections. The use of appropriate materials and sturdy build ensures these systems perform effectively in preventing workplace falls.
In conclusion, passive fall protection systems play a crucial role within the hierarchy of fall protection, offering a reliable and hands-off approach to safety. By integrating guardrails, safety nets, and barriers, workplaces can maintain safety, reduce accidents, and safeguard their workforce effectively.
Fall Restraint Systems
Fall restraint systems are an integral part of the hierarchy of fall protection. They serve as proactive solutions that prevent workers from reaching hazardous areas at heights. Unlike fall arrest systems, which act after a fall occurs, restraint systems stop falls from happening in the first place. These systems form a vital defense mechanism when elimination or passive systems are not viable options.
How Restraint Systems Work
Fall restraint systems work by restricting a worker’s movement to keep them away from fall hazards. These systems involve anchorage points, connectors, and harnesses that limit access to dangerous areas. Workers remain securely tethered, ensuring they cannot accidentally position themselves near edges or open areas.
For effective use, employers must assess workplace hazards and determine appropriate working zones. Proper setup ensures that restraint systems block access to all high-risk areas. Correct training on how to use these systems also plays a key role in maximizing safety. Such measures ensure workers operate confidently without exposure to potentially dangerous zones.
Typical Equipment Used in Restraint Systems
Fall restraint systems rely on specific equipment to function effectively. Common components include:
- Harnesses: Full-body harnesses secure workers and evenly distribute force, minimizing discomfort during use.
- Lanyards: Lanyards connect harnesses to anchor points, restricting movement beyond safe boundaries.
- Anchorage Points: Strong, fixed points are vital for system stability, ensuring the tethering mechanism functions correctly.
- Rope Grabs: Adjustable rope grabs are sometimes used to allow limited movement within a safe working zone.
Employers must ensure all equipment meets safety standards and is inspected regularly for wear and tear. High-quality materials and proper installation are critical for reliable performance. Additionally, workers should receive training on using and maintaining the equipment to avoid misuse.
By implementing fall restraint systems, workplaces can effectively stop potential falls. These systems offer a practical, worker-focused approach to maintaining safety, aligning with the hierarchy of fall protection’s preventive principles.
Fall Arrest Systems
Fall arrest systems are essential tools within the hierarchy of fall protection. They are designed to stop falls after they occur, minimizing injury risks. These systems act as active protection when elimination, passive systems, and fall restraint solutions are not possible. Their effectiveness ensures worker safety in high-risk environments like construction sites and roof work areas.
Key Components of Fall Arrest Systems
Fall arrest systems rely on specific components that work together to prevent injuries during a fall. These components include:
- Anchor Points: Secure, fixed points where the system attaches, providing stability during use.
- Harnesses: Full-body harnesses designed to spread fall forces evenly and reduce injury.
- Lanyards: Shock-absorbing lanyards minimize force during a fall and connect harnesses to anchors.
- Lifelines: Flexible lines used to provide mobility while keeping the worker within a protected zone.
- Deceleration Devices: Devices like shock-pack lanyards or self-retracting lifelines slow the fall rate.
Employers must ensure all components meet safety standards and are properly maintained. Regular checks ensure these systems operate effectively and remain reliable over time.
When and How to Use Fall Arrest Systems
Fall arrest systems should be used when workers must operate in environments with unavoidable fall risks. These systems are critical for tasks performed at elevated heights such as:
- Roof inspections and repairs.
- Working on unprotected edges.
- Using scaffolds without guardrails.
Proper usage involves careful planning and training:
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify work areas where fall arrest systems are necessary.
- Use Correct Setup: Secure anchors, inspect equipment, and adjust harnesses for a proper fit.
- Provide Training: Teach workers how to use and inspect fall arrest systems.
- Supervise Work Areas: Ensure ongoing oversight to minimize human errors.
Employers should also develop emergency response plans for situations when a fall occurs. By using fall arrest systems properly, workplaces can protect employees and comply with safety regulations like OSHA and ANSI standards.
Fall arrest systems are a lifeline for workers exposed to hazardous heights. Their proper implementation showcases an organization’s commitment to safety while demonstrating adherence to the fall protection hierarchy.
Administrative Controls and Training
Administrative controls and training are a critical component of the hierarchy of fall protection. These methods involve establishing safety policies, educating workers, and providing oversight to prevent falls. Unlike physical systems, administrative controls focus on behavior and processes to ensure workplace safety.
Developing Safety Protocols and Training Programs
Safety protocols and training programs form the backbone of administrative controls. They provide workers with the knowledge and guidance needed to avoid fall hazards.
- Create Comprehensive Safety Policies: Establish clear steps to manage fall risks. For example, define access restrictions and mandatory equipment use.
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct inspections to identify evolving safety hazards. Update protocols based on new findings regularly.
- Worker Training: Provide thorough training on fall prevention methods and equipment usage. Include practical demonstrations.
- Emergency Response Plans: Develop steps for rescuing workers in fall-related emergencies. Train workers to act quickly.
Clear and concise safety protocols reduce confusion among workers. Training ensures they are confident in identifying and managing situations prone to fall risks.
Role of Supervision and Monitoring
Supervision and monitoring ensure that safety protocols and training are effectively implemented.
- On-Site Supervision: Assign supervisors to oversee compliance with fall protection procedures during work hours.
- Routine Safety Audits: Conduct regular checks to ensure workers follow established protocols and use safety systems correctly.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Encourage workers to report unsafe conditions and suggest improvements to safety measures.
- Corrective Action Plans: Address lapses in safety compliance swiftly through clear procedures and consequences.
By maintaining strong oversight, employers reinforce the importance of adhering to safety standards. Monitoring fosters a culture of accountability and proactive fall prevention.
Administrative controls work best when integrated with physical safety measures. Together, they create a well-rounded approach to fall protection, reducing injuries and ensuring workplace compliance.
Maintaining and Inspecting Fall Protection Systems
Fall protection systems require regular upkeep to ensure their effectiveness and worker safety. Proper inspection and maintenance processes reduce risks and extend the lifespan of equipment. Employers must implement robust practices for monitoring these systems.
Regular Inspection Checklist
Regular inspections are essential to identify wear, damage, or deterioration in fall protection systems. Follow this checklist to ensure safety:
- Check Harness and Belts: Inspect for tears, cuts, or fraying.
- Examine Lanyards: Look for broken stitching or signs of abrasion.
- Verify Anchor Points: Ensure anchor points are secure and free from corrosion.
- Inspect Connections: Validate the proper functioning of buckles, hooks, and attachment points.
- Assess Lifelines: Confirm they are intact and free from damage.
- Test Deceleration Devices: Ensure shock-absorbing components are not compromised.
- Check Safety Nets: Look for tears or loose attachments.
Inspections should be documented clearly. Replace or repair damaged components immediately to prevent accidents. Employees should be trained in recognizing equipment issues during their routine checks.
Importance of Maintenance to Ensure Safety
Maintenance ensures fall protection systems remain reliable and safe over time. Neglected systems can lead to serious hazards. Key reasons for effective maintenance include:
- Preventing Failures: Proper upkeep ensures equipment works correctly during emergencies.
- Extending Equipment Lifespan: Regular care prevents premature wear.
- Cost Efficiency: Routine maintenance reduces unexpected repair costs.
- Compliance with Regulations: Maintained systems align with OSHA and ANSI requirements.
Employers must set maintenance schedules based on equipment use. Tasks should include cleaning, lubrication, and adjustment of components. Certified professionals should handle complex repairs or replacements. Employers should also ensure workers use maintenance logs with precise records.
By conducting thorough inspections and following maintenance routines, workplaces can improve safety and avoid unnecessary risks. This approach reduces accidents, enhances trust in systems, and promotes a proactive safety culture. Regular care highlights the commitment to minimizing fall hazards effectively.
Compliance with Legal Standards
Compliance with legal standards ensures the safety of workers and avoids costly penalties. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) set specific guidelines for fall protection in workplaces. Adhering to these standards is essential for fostering a safe working environment.
Overview of OSHA and ANSI Regulations
OSHA and ANSI provide clear regulations to minimize fall-related risks. These rules outline the proper use of fall protection systems and procedures.
- OSHA Standards: OSHA mandates fall protection for workers operating at heights of six feet or more. Employers must use proper fall protection systems, such as guardrails, safety nets, or personal fall arrest systems. Regular training and equipment inspections are also required.
- ANSI Standards: ANSI provides detailed requirements for the design, testing, and use of fall protection equipment. ANSI standards ensure that harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points meet quality guidelines. These standards also emphasize qualified supervision during operations at height.
Both organizations aim to reduce fall-related injuries and fatalities. Employers have a legal obligation to comply with these standards to create a safer work environment.
Meeting Workplace Safety Legal Requirements
Meeting legal safety requirements involves active effort and regular reviews. Employers must implement policies and procedures aligned with regulations.
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Identify fall hazards through thorough workplace inspections and assessments.
- Provide Certified Equipment: Ensure all equipment used meets OSHA and ANSI standards.
- Train Workers Regularly: Conduct frequent training sessions to teach correct equipment use and fall prevention methods.
- Maintain Records: Document safety inspections, equipment maintenance, and training sessions to demonstrate compliance.
- Supervise Work Sites: Assign trained supervisors to monitor safety practices in high-risk areas.
- Stay Updated on Standards: Regularly review updates to OSHA and ANSI guidelines to ensure compliance.
By following these steps, employers can protect their workers and avoid violations. Compliance with legal standards also reinforces a company’s commitment to safety and operational excellence.
In conclusion, adherence to OSHA and ANSI regulations is critical for creating safe workplaces. Understanding and meeting these requirements helps reduce falls, protect employees, and maintain legal compliance.
Conclusion
Summary of the Fall Protection Hierarchy
The hierarchy of fall protection provides a structured approach to workplace safety. It starts with eliminating hazards, offering the most reliable solution. Passive systems like guardrails and safety nets come next, creating physical barriers. Fall restraint systems restrict access to hazardous zones, preventing falls before they happen. Fall arrest systems stop falls after they occur, reducing injury risks. Administrative controls and training focus on behavior, ensuring policies and protocols enhance safety. Together, these levels form a comprehensive strategy to manage fall hazards effectively.
Emphasizing the Goals of a Safe Workplace
A safe workplace protects employees and ensures operational efficiency. Employers must prioritize hazard awareness and proactive safety measures. By following the hierarchy of fall protection, companies can reduce injuries and boost worker confidence. Compliance with OSHA and ANSI standards ensures legal adherence while promoting a culture of safety. Remember, the ultimate goal is to save lives, enhance trust, and maintain productivity. With continuous effort, employers can create a workplace where safety is always the top priority.